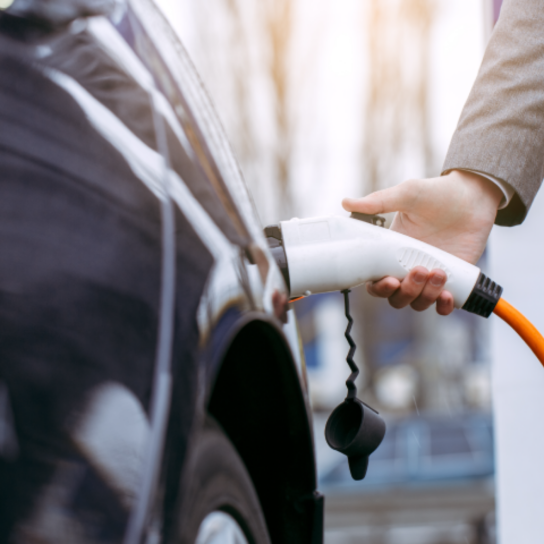
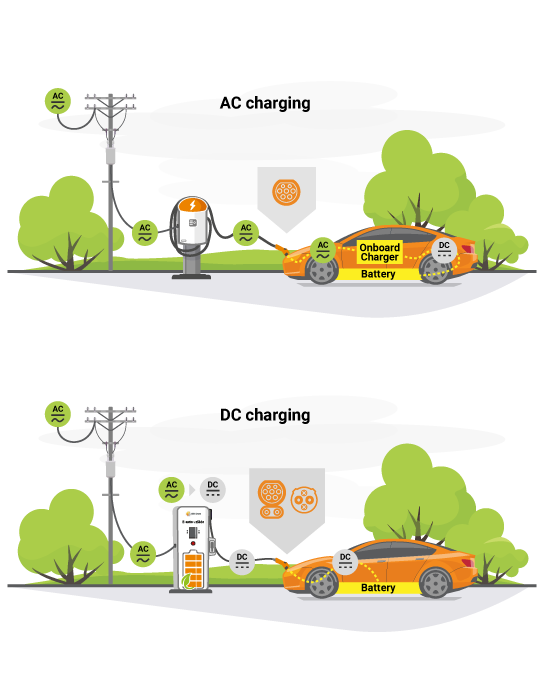
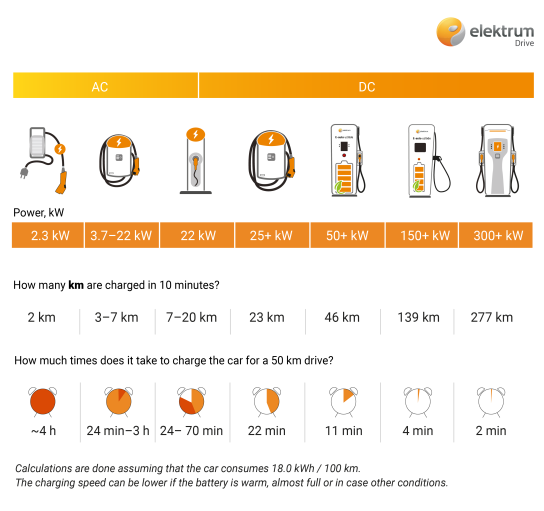
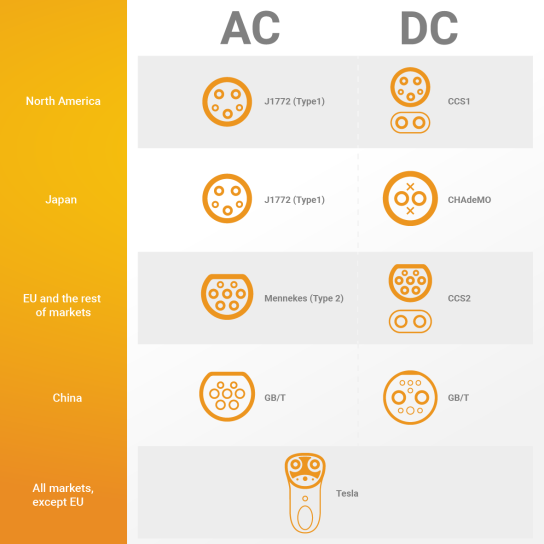
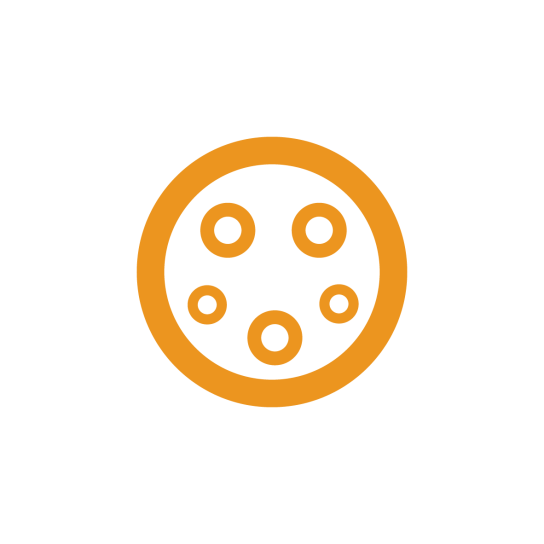
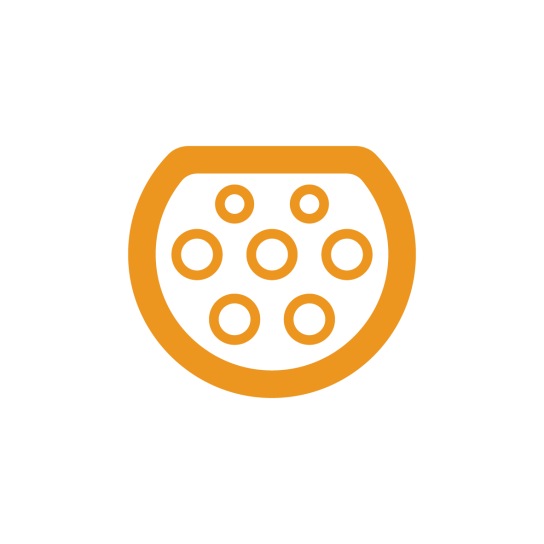
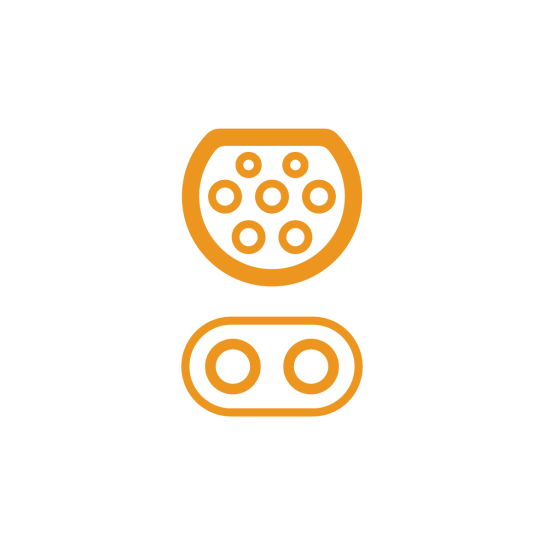
Medium fast charging is characterised by a power from 3.7 kW to 22 kW, which typically allows to charge an electric car within 3 to 6 hours, depending on the available charging power and the battery capacity of the electric car.
The charging solution uses a special charging device, that is most often mounted on a building wall or on a post. A charging device provides an opportunity to charge an electric car at least twice as fast, adjust the charging capacity to the electrical network connection capacity, perform electricity metering, program charging at night, etc.
Unlike a household Schuko 230V socket, this charging solution requires the work of a certified electrician. It should be noted that not all electric car chargers are designed for such power.
Medium fast charging stations are suitable for places where the electric car is parked for about 3 hours or more. These include public charging points, supermarket car parks, entertainment venues and territories of office buildings. When purchasing an electric car with a high-capacity battery, it would be useful to install such a charging station in your private house in order to be able to fully charge the car at night hours if necessary.